3 C’s Framework: A strategic analysis tool used to assess a business situation by examining three critical components: Customers, Competition, and the Company. This framework is particularly valuable in contexts such as market entry, mergers and acquisitions, product development, and launching new ventures.
4 P’s Analysis: A marketing framework used to evaluate a product’s marketing strategy by examining four critical components: Price, Product, Promotion, and Place.
5 C’s of Credit: A framework for assessing borrower creditworthiness based on five factors—Character (trustworthiness), Capacity (ability to repay), Capital (personal investment), Collateral (assets pledged), and Conditions (economic and loan context).
9 M’s Resource Audit: A strategic tool that categorizes an organisation’s resources into nine areas—Materials, Machinery, Make-up, Management, Management Information, Markets, Men and Women, Methods, and Money—to assess internal capabilities.
10,000-Foot View: A high-level overview of a situation, focusing on the big picture rather than detailed specifics.
Acronym: An abbreviation formed from the initial letters of other words and pronounced as a word. For example, “PEST” stands for Political, Economic, Social, and Technological, which are the four factors for a business to consider when scanning the business environment (see PEST Analysis).
Adverse Selection: A situation where sellers have information about some aspect of product quality that buyers do not have, or vice versa. For example, it can lead to high-risk individuals being more likely to purchase insurance, thereby increasing overall costs.
Aggregator: A business model that not only facilitates interactions between third parties but also actively intermediates and controls the relationship. Companies like Alphabet (Google) and Facebook curate content and optimise advertising placements, directly influencing user experience.
Anchoring: A cognitive tendency where individuals rely too heavily on the first piece of information encountered (the “anchor”) when making decisions, even if it’s irrelevant. This can significantly impact negotiations and pricing strategies.
Ansoff Matrix (Product/Market Expansion Grid): This tool assists businesses in determining growth strategies by focusing on existing or new products and markets, leading to four strategic options: market penetration, market development, product development, and diversification.
Asset (accounting definition): An economic resource that a company uses to operate its business, e.g. cash, inventories, and equipment.
Asset (investing definition): Something that puts money in your pocket every month (i.e. your house and your car are not assets).
Barriers to entry: The obstacles that must be overcome and the costs that must be paid by a new market entrant but not by firms already in the industry. Barriers to entry may exist due to: capital requirements, economies of scale, product differentiation (e.g. brand loyalty), intangible assets (e.g. patents), access to suppliers, access to distribution channels, or regulatory policies.
BCG Growth-Share Matrix: A strategic tool developed by the Boston Consulting Group to assist companies in analysing their product or business unit portfolios. It categorises offerings based on market growth rate and relative market share, guiding resource allocation decisions. See also: Stars, Cash Cows, Question Marks, and Dogs.
Black Swan: An event that is unpredictable, has significant consequences, and is (or at least appears to be) retrospectively explainable. The term “Black Swan” was coined by Nassim Nicholas Taleb in his book The Black Swan.
Bootstrapping: A method of financing a business by using personal finances or the company’s operating revenues, rather than seeking external investors. This approach is common among startups aiming to maintain control and avoid dilution of ownership.
Brand: What people say about you (or your organisation) when you’re not in the room.
Bund: The German government’s federal bond, similar to Treasury bonds in the U.S.
Business Mutualism: An association between two or more separate enterprises, or fields of activity, where (1) each enterprise benefits the other, and (2) collective discoveries emerge beyond those of any single field.
Cash Cows: Business units with high market share in low-growth markets. These are established, profitable units generating more cash than needed, often funding other segments.
CFA: Stands for “Chartered Financial Aanalyst”. For more information, visit the CFA Institute.
Choice Theory: This psychological framework developed by William Glasser posits that human behaviour is driven by five basic needs: survival, love and belonging, power, freedom, and fun. Understanding these needs can enhance motivation strategies within organisations.
Coase theorem: If trade in an externality is possible and there are no transaction costs, bargaining will lead to an efficient outcome regardless of the initial allocation of property rights. In practice, obstacles to bargaining or poorly defined property rights can prevent Coasian bargaining.
Coin Flip, The: A decision-making technique that leverages emotional responses to clarify preferences. By assigning options to the outcomes of a coin toss and observing your immediate emotional reaction to the result, you can uncover your true inclination. This method acknowledges that while logic informs our thoughts, emotions drive your actions, and thus, understanding your emotional response can lead to more authentic decisions.
Collectively Exhaustive: Where information is being grouped into categories, all categories taken together are said to be “collectively exhaustive” if all relevant information falls into one or more categories.
Commercial Awareness: An understanding of how businesses operate, in the context of today’s social, political, and economic climate.
Comparative Advantage: A country has a comparative advantage in producing a good if it can produce that good at a lower opportunity cost than any other country.
Competitor-Based Pricing: Setting prices in line with or in response to competitors’ pricing strategies. This can involve pricing below competitors to gain market share, matching prices to remain competitive, or pricing above competitors to signal higher quality. The pricing strategy is often used in markets with high competition.
Complimentary goods: Any goods for which an increase in demand for one leads to a increase in demand for the other. Examples of complimentary goods might include printers and ink cartridges, DVD players and DVDs, and Microsoft Windows and PCs.
Confirmation bias: A tendency of people to favour information that confirms their existing beliefs.
Consumer Surplus: The difference between what consumers are willing to pay for a good or service and what they actually pay. It represents the extra benefit or utility gained by consumers in a transaction.
Context Window: The curated set of information presented to a user at a specific moment, tailored to their current task, intent, and environment.
Convex Tinkering: A term popularised by Nassim Taleb, describing a trial-and-error approach where numerous low-cost “mistakes” are made, leading occasionally to significant breakthroughs. This process underscores the value of experimentation and adaptability in learning.
Cost-Based Pricing: Setting a product’s price by adding a markup to its production cost to achieve a desired profit margin. This approach considers both variable and fixed costs, allocating them appropriately to determine the final price.
Cost benefit analysis: An analysis framework that involves weighing up the total expected costs and benefits of one course of action against another.
Credit default swap (CDS): A form of insurance policy which obliges the seller of the CDS to compensate the buyer in the event of loan default. In the event of default, the buyer of the CDS would normally receive money and the seller of the CDS would receive the defaulted loan (and the right to recover amounts outstanding under the loan).
Cross Rate: The exchange rate between two currencies inferred from each currency’s exchange rate with a third currency.
Customer Journey Map: A visual representation that outlines the steps a customer takes when interacting with a company, from initial contact through to purchase and beyond.
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): A prediction of the net profit attributed to the entire future relationship with a customer. CLV helps businesses understand the long-term value of customer acquisition and retention strategies.
Design thinking: An iterative approach to innovation that typically unfolds through five key stages.
- Empathise – Observe and engage with users to gain insight.
- Define – Synthesize findings into a clear problem statement.
- Ideate – Generate a wide array of creative solutions.
- Prototype – Build tangible models to explore ideas quickly and cheaply.
- Test – Evaluate prototypes with users, gather feedback, and improve.
Dogs: Business units with low market share in low-growth markets. These units typically neither generate nor consume substantial cash and may be candidates for divestiture.
Debt: A form of financial leverage which can be used to increase your ability to consume or invest.
Differentiation: A strategy that sets a product apart from competing products in the minds of customers by emphasising unique attributes such as quality, features, reliability, availability, or branding—enabling the product to offer additional perceived value in the eyes of customers.
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF): A valuation method estimating the present value of future cash flows.
Discouraged worker: A person who does not have a job and is available to work but who has stopped actively looking for work. This may happen because an unemployed person:
- becomes discouraged due to previous unsuccessful attempts to obtain work;
- believes (reasonably or not) that there are no jobs available in their industry or location;
- lacks the skills needed for the jobs which are available, either because they never had the required skills or because their skills have eroded due to a long period of unemployment;
- is discriminated against by prospective employers for some reason beyond their control (e.g. age, race, gender); or
- becomes addicted to Twinkies and day time television. This one sounds like a joke, but it is conceivable that after a period of prolonged unemployment a person who previously had an aversion to receiving welfare payments could become welfare dependent.
Diseconomies of scale: A situation where the average cost of production increases as output increases.
Disruptive Innovation: A process by which a product or service initially takes root in simple applications at the bottom of a market and then consistently moves ‘up market’, eventually displacing established competitors. Coined by Clayton Christensen.
Diversification: The most risky growth strategy, diversification entails developing new products for new markets. This approach requires careful analysis of market growth potential and industry attractiveness to mitigate risks. See also: Horizontal diversification, Lateral diversification, and Vertical integration.
Due Diligence: The comprehensive appraisal of a target company, covering financials, operations, legal matters, and other critical areas to ensure informed decision-making.
Due Diligence (DD): A critical phase in an M&A deal aimed at validating the information provided by a target company, identifying key risks, and assessing the attractiveness of the investment opportunity. DD involves the comprehensive appraisal of a target company, covering financials, operations, legal matters, and other critical areas to ensure informed decision-making.
Economic indicator: Any economic statistic (e.g. the unemployment rate, GDP, or the inflation rate), which indicates the current strength of the economy and/or the future expected performance of the economy.
Economies of Scale: A situation where the average cost of producing one unit of a good or service decreases as the quantity of output increases.
Economies of Scope: Cost advantages that a business obtains due to a broader scope of operations, such as producing multiple products together more cheaply than separately. It’s distinct from economies of scale, which relate to cost savings from increased production volume.
Elevator pitch: A high-level overview of whatever it is that you are selling and is designed to just get the conversation started. See also: 12 Tips for Creating an Effective Pitch.
Equity: The net worth of a company equal to Assets minus Liabilities. Equity holders are the owners of the business.
Expenses: Costs incurred by a business over a specified period of time to generate the revenues earned during the same period.
Experience Curve: A concept illustrating that as a company gains production experience, its performance tends to improve at a predictable rate. This suggests that, despite the randomness of individual learning events, overall organisational learning can follow a consistent pattern over time.
Externality: A cost or benefit which is incurred by a person who did not agree to the activity which caused the cost or benefit. Externalities that confer a benefit are referred to as “positive externalities”; externalities that impose a cost are referred to as “negative externalities”. When externalities exist, the market price of the good or service will not reflect the full social cost or benefit.
First-Mover Advantage: The competitive edge gained by being the first to enter a particular market or industry. This can lead to brand recognition, customer loyalty, and control over resources. However, it also comes with risks like market uncertainty.
Fiscal Policy: Government policy as it relates to government spending and taxes.
Fixed cost: A cost that do not vary with the quantity of output produced. It is important to understand that fixed costs are fixed only in the short term. In the long run nearly all costs are variable: a company can renegotiate its supply contracts or move its factories to a country with lower costs of production.
Free rider problem: a situation where individuals or firms can benefit from a good, service, or resource without paying for it. This leads to under-provision of the good by the free market. Government provision is a possible solution. National defence is a popular example, once it is provided, everyone in society benefits from security, whether or not they paid taxes.
Gains from Trade: The net benefits that both consumers and producers receive from engaging in voluntary trade. It reflects the idea that trade can make all parties better off.
GE-McKinsey 9-Box Matrix: A strategic portfolio analysis tool, developed by McKinsey for General Electric in the 1970s, that assists multi-business corporations in evaluating and prioritising investments across business units by assessing two key dimensions: industry attractiveness and competitive strength. The matrix plots business units within a 3×3 grid, categorising them into nine cells that inform strategic actions—such as invest/grow, selectivity/earnings, or harvest/divest—to optimise resource allocation and long-term profitability.
Greenspan Put: The monetary policy of Alan Greenspan and the Federal Reserve from the late 1980’s to the mid-2000’s, which involved significantly lowering interest rates in the wake each financial crisis.
Hypothesis-Based Problem Solving (HBPS): A structured method that starts with a clearly defined problem and tests hypotheses about root causes and solutions through focused, data-driven analysis. Steps include defining the problem, forming hypotheses, identifying data needs, analysing evidence, and forming recommendations.
Homogenous product: Any good or service for which buyers perceive no difference between the products offered by different suppliers. For example, wheat, corn and oil.
Horizontal diversification: A situation where a company adds new products, often unrelated to its existing products, that may appeal to existing customers. This strategy may increase the company’s dependence on certain market segments.
Industrial organisation: Industrial organisation is a field in economics which examines the structure of firms and markets.
Inflation: An increase in the overall price level over a period of time.
Internal Rate of Return (IRR): The discount rate that makes the net present value of all cash flows from a particular project equal to zero.
Investment banking: A profession that involves raising money to allow a company to grow its business. This money might be raised by selling securities (stocks and bonds).
Investment operation: An operation which, upon thorough analysis, promises safety of principal and an adequate return. Operations not meeting these requirements are speculative (Ben Graham, The Intelligent Investor).
Joint production: Production where the production process for two or more different goods is connected. Producing the goods separately would result in increased costs. Joint production may occur naturally: for example, a chicken farm produces both chicken wings and chicken breasts. Joint production may also be used because it provides economies of scope.
Lateral diversification: A situation where a company moves beyond the confines of the industry to which it belongs. Sometimes referred to as “conglomerate diversification”.
Law of Large Numbers: A statistical principle stating that as the number of trials increases, the average of the results becomes more predictable. Applied to the concept of the Experience Curve, it explains how individual learning variances tend to average out, resulting in a stable organisational learning rate.
Learning from Experience: A natural, unstructured process through which individuals and organisations improve by engaging in activities, observing outcomes, and adapting accordingly. This form of learning often occurs serendipitously, without formal instruction, as people discern what works and what doesn’t through direct involvement.
Leverage (investment definition): The use of borrowed capital to partially or fully fund an investment. Leverage is used when an investor expects the return on investment (ROI) to be greater than the cost of debt, in which case the investor’s return on equity (ROE) will be greater than the ROI. You could say the returns are leveraged.
Leveraged Buyout (LBO): A financial transaction where a company is acquired using a significant amount of borrowed money.
Liability (accounting definition): The debt of a company, a claim that creditors have on the company’s resources.
Liquidity trap: A situation where interest rates are zero (or near zero) and a central bank is no longer able to stimulate the economy by controlling short term interest rates. In 2008, the Federal Reserve was faced with a liquidity trap and employed quantitative easing to stimulate the economy.
Loss aversion: Refers to a commonly observed behavioural trait whereby people would prefer to avoid a loss than to make a commensurate gain.
Ludic Fallacy: A term coined by Nassim Nicholas Taleb in The Black Swan. The term refers to the misuse of games to model real-life situations. Taleb explains the fallacy as “basing studies of chance on the narrow world of games and dice.”
Madoff Scheme: See Ponzi Scheme.
Management consulting (Tom’s definition): A profession that aims to assist management by (a) providing expert knowledge, (b) facilitating the examination of business problems, (c) implementing solutions, and (d) supporting organisational change.
Management consulting (Institute of Management Consultants’ definition): The provision to management of objective advice and assistance relating to the strategy, structure, management and operations of an organisation in pursuit of its long-term purposes and objectives. Such assistance may include the identification of options with recommendations; the provision of an additional resource and/or the implementation of solutions.
Map of Life: A strategic storytelling framework that guides teams to define a product’s purpose, audience, team capabilities, and solution by answering four key questions: Why (purpose), For Whom (target users), Who (team strengths), and What (product offering). Adapted from the Design Council’s Double Diamond model and inspired by Simon Sinek’s “Start With Why”, it helps align vision, differentiate offerings, and craft compelling product narratives.
Market Analysis: Evaluating the broader market dynamics to determine the potential success or failure of an acquisition. This includes assessing market size, growth rate, profitability, competition intensity, barriers to entry, and regulatory environment.
Market Development: An approach that involves introducing existing products into new markets. New markets can encompass different geographical regions, customer segments, or distribution channels.
Market Penetration: A strategy focused on increasing sales of existing products within existing markets. This can be achieved through various initiatives related to pricing, product enhancements, distribution channels, and promotional activities.
Market Study Framework: Utilised in case interviews and strategic analysis, this framework assesses market attractiveness through four lenses: Economy (macro-environment), Industry (competitive landscape), Company (internal capabilities), and Project (specific initiatives).
McKinsey 7 S Framework: A diagnostic tool that provides a guide for organisational change, it describes seven factors which together determine the way in which an organisation operates: shared values, staff, skills, style, strategy, structure, and systems.
MECE: Mutually exclusive, collectively exhaustive.
MECE Analysis: The idea that, when analysing a business problem, issues should be divided into groups so that each grouping is separate and distinct (mutually exclusive), and all groups taken together should comprehensively represent all of the issues related to the problem at hand (collectively exhaustive).
Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A): The process of combining two companies into one, aiming to achieve synergy—where the combined entity is more valuable than the sum of its parts.
Mnemonic: A system or technique that is designed to aid the memory.
Money: Anything that is generally accepted in payment for goods or services, or in the repayment of debts.
Monopoly: A situation where a market has only one supplier for a particular good or service. Monopolies are characterised by a lack of competition and a lack of viable substitutes.
Moral Hazard: Any situation where a person or organisation is not fully responsible for the consequences of its actions. As a result, the person or organisation may take greater risks than it otherwise would because it is not responsible for paying the full cost if things go badly.
Mortgage Securitisation: A process which involves three steps:
- purchasing mortgages from banks and mortgage brokers;
- grouping these mortgages together into large pools; and then
- selling “shares” in these mortgage pools to investors.
Mutually Exclusive: Where information is being grouped into categories, categories are said to be “mutually exclusive” if information cannot be placed in more than one category. E.g. “revenue” and “expenses” are mutually exclusive categories.
Neologism: A newly coined word or phrase that might be in the process of entering common usage, but has not yet been accepted into mainstream language. E.g. “business mutualism”.
Net Asset Value (NAV): Calculates the value of a company’s assets minus its liabilities.
Net Present Value (NPV): A financial metric that calculates the present value of a series of future cash flows generated by an investment, minus the initial investment cost. It is used to assess the profitability of an investment, with a positive NPV indicating a potentially profitable venture.
Network effects: The situation whereby a product or service becomes more valuable as more people use it (also known as network externalities). One example is eBay; as more buyers use the online auction site it becomes more valuable to each seller, and as more sellers use the site it becomes more valuable to each buyer.
NINJA Loan: Any loan made where the borrower has No Income, No Job, and No Assets.
Nominal value: A value expressed in dollar terms. For example, if a Big Mac costs $3 this year and $6 next year, then we would say that the nominal price of the BigMac has doubled.
NPV (net present value): The net present value of an investment is the present value of the series of cash flows generated by the investment minus the cost of the initial investment.
Numéraire: An economic term which refers to “the unit of account”. In French, the term means “money”, “coinage” or “face value”. A country’s currency normally acts as the numéraire and is used to measure the worth of other goods and services within the country. In the absence of currency, you could define a “numéraire good” (e.g. salt, copper, gold) to have a fixed price of 1; the worth of other goods and services can then be measured relative to the numéraire good.
Oligopoly: A situation where a market is dominated by a small number of suppliers for a particular good or service. Oligopolies are characterised by a lack of competition and a lack of viable substitutes. Each firm in an oligopoly must take into account the likely actions and reactions of other firms when developing its strategic plan.
Opportunity cost: The opportunity cost of an item is what must be given up to obtain that item.
Option: A derivative financial instrument which grants its owner the right, but not the obligation, to purchase or sell an underlying asset at a pre-established price for a specified period of time.
Organic growth: Growth that a company can achieve by increasing output and sales. This excludes growth achieved as a result of mergers and acquisitions since these profits are not generated internally (e.g. if Facebook achieves growth as a result of its purchase of Whatsapp then this would not be considered organic growth).
Outsourcing Matrix: A strategic framework that assists firms in evaluating which activities to retain in-house, outsource, or eliminate, based on two dimensions: strategic importance and operational performance contribution.
Overconfidence bias: Refers to a behavioural trait whereby a person’s confidence in their opinions is invariably higher than the accuracy of their opinions.
PPP Model (People, Process, Place): A healthcare improvement framework that enhances the patient experience by focusing on three key dimensions: the behaviour and engagement of staff (People), streamlined and patient-centred workflows (Process), and a calming, functional physical environment (Place).
Pareto efficient: An economic allocation is said to be “Pareto efficient” if no person can be made better off without making at least one person worse off. Pareto efficiency does not imply that an economic allocation is fair or equitable.
Pareto Principle (80/20 Rule): The principle that roughly 80% of effects come from 20% of causes. In business, this might mean that 80% of sales (or profits) come from 20% of clients, guiding managers to focus on the most impactful areas.
Perspicacity: A keenness of perception and the ability to draw sound conclusions; to be insightful, shrewd, and discerning.
PEST Analysis: A framework used to analyze the external environment by examining Political, Economic, Social, and Technological factors.
Platform: A business model that facilitates interactions between third parties, earning revenue by capturing a share of the value created in these interactions. Examples include Uber and Airbnb, which connect service providers with customers.
Ponzi Scheme: Any kind of fraudulent investment operation that pays returns to investors from their own money or money paid by subsequent investors rather than from any profits earned.
Porter’s Five Forces: A framework used to determine the competitive intensity and attractiveness of an industry, it considers five forces affecting the competitive pressure exerted on a business: existing competition, barriers to entry, substitutes, customer bargaining power, and supplier bargaining power.
Porter’s Generic Strategies: A strategic framework that outlines three core ways a firm can gain competitive advantage: Cost Leadership (offering the lowest price through efficient operations), Differentiation (offering unique value through product features, brand, or service), and Focus (targeting a specific market niche with either a cost or differentiation approach). Firms must choose one to avoid being “stuck in the middle” with no clear advantage.
Porter’s Six Steps of Strategic Positioning: An extension of Porter’s generic strategies, this framework outlines steps for achieving a sustainable competitive advantage, including performing different activities from rivals and ensuring all activities reinforce the company’s strategy.
Power User: A product user who return frequently, unlocks advanced features, and refer others.
Price taker: A firm that can change its production and sales of a product without significantly affecting the market price.
Priority Matrix: A decision-making tool that categorises tasks based on their impact and complexity, helping organisations prioritise initiatives that offer the most significant benefits relative to their implementation effort.
Product Development: A strategy aimed at developing new products to cater to existing markets. This involves innovation and product enhancements to meet the evolving needs of the current customer base.
Product Differentiation: The process of describing the differences between a good or service in order to demonstrate the unique aspects of your good or service and create an impression of value in the mind of the consumer.
Product Life Cycle Model: A framework that outlines the progression of a product through four stages—Introduction, Growth, Maturity, and Decline—each characterised by distinct market dynamics, sales patterns, and strategic considerations. This model aids businesses in tailoring marketing, pricing, and operational strategies to align with the product’s current stage, thereby optimising profitability and resource allocation.
Product Roadmap: A strategic document that outlines the vision, direction, priorities, and progress of a product over time. It aligns product development with business goals and customer needs, serving as a communication tool for stakeholders.
Profitability Framework: A diagnostic tool used to identify and address the root causes of declining profitability by analysing revenue and cost components.
Profit Maximisation: A fundamental goal for firms, achieved by adjusting price and quantity to maximise the difference between total revenue and total cost. Some firms may have different goals. For example, firms with high fixed costs like Amazon may choose to maximise sales. The overarching goal is to maximise the value of the firm for shareholders, but there may be a conflict between maximising this value in the short run versus the long run.
Public good: A good which is non-rival and non-excludable. Non-rivalry means that consumption of the good by one individual does not reduce availability of the good for other to consume; and non-excludability means that no one can be excluded from using the good. In the real world, there may be no goods which are absolutely non-rival and non-excludable.
Question Marks: Business units with low market share in high-growth markets. These units consume resources and require careful analysis to determine if they can become Stars or should be divested.
Real value: A value adjusted for inflation or deflation. For example, if a Big Mac costs $3 this year and $6 next year, then assuming inflation is 100% the real price of the BigMac has not changed.
Recession: Broadly speaking, a recession is a period of slow or negative economic growth, usually accompanied by rising unemployment. Economists have other more precise definitions of a recession, the easiest of which to understand is “two consecutive quarters of falling GDP”. For more information, read the article: Economic recession 2008: measuring the strength of the economy. Alternatively, visit the Economist A-Z.
Remarkable: Something that is worth people making a remark about. Are you doing something remarkable?
Replacement value: An estimate of how much it would cost to build equivalent resources or capabilities from scratch.
Return on Investment (ROI): a financial performance metric that measures the profitability of an investment, expressed as a percentage of the original amount invested.
Revenue: Income generated from trading or, for example, selling off a piece of the business or a piece of equipment. Revenue is recorded when the sale is made as opposed to when the cash is received.
Résumé: A document which summarises your background and accompanies your cover letter as part of your job application.
Serendipity: A happy and unexpected event (or discovery) that occurs by accident.
SMART Goals: Any goal which is Specific, Measureable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-Bound.
Spillover: Externalities that result from economic activity and affect people who are not directly involved in the activity. Spillover can be positive or negative. Pollution that leaks out of a manufacturing plant and into a local river would have a negative spillover effect on local fishermen. The beauty of the buildings in Oxford would have a positive spillover effect on locals and tourists.
STAR Framework: A structured method for answering behavioural and competency-based interview questions clearly and concisely. STAR stands for Situation (the context), Task (what needed to be done), Action (the steps you took), and Result (the quantified result, e.g. sales growth rate, dollars of profit).
Stars: Business units with high market share in high-growth markets. These units are leaders requiring significant investment to sustain growth but have the potential to become Cash Cows as the market matures.
Strategic partnership: A structured, long-term collaboration between two or more organizations that align around shared goals and complementary capabilities.
Substitute goods: Any goods for which an increase in demand for one leads to a fall in demand for the other. Substitute goods represent a form of indirect competition. Examples of substitute goods might include Coca-Cola and Pepsi or Vegemite and Nutella.
Sunk cost: An expenditure that has already been paid and which cannot be recovered.
Switching costs: Any real or perceived costs that a consumer incurs (e.g. money, time, effort) as a result of changing suppliers, brands, or products.
SWOT: Strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats.
SWOT analysis: A strategic planning tool used to evaluate the strengths (S), weaknesses (W), opportunities (O), and threats (T) involved in a business venture. It involves specifying the objective of the business venture and identifying the factors that are expected to help or hinder the achievement of that objective.
Synergy: The concept that the combined performance and value of two companies will be greater than the sum of the separate individual parts.
TARP: The US$700 billion Troubled Asset Relief Program created by the US government in 2008 in the wake of the sub-prime mortgage crisis.
Underemployment: A situation where a person’s capacity to work is not fully utilised. This may occur for three reasons: (1) over-qualification, (2) involuntary part-time work, and/or (2) over-staffing.
Up or Out Policy: A career progression model in consulting firms where consultants must advance to the next level within a set timeframe or exit the firm, promoting a meritocratic culture and maintaining a pyramid organisational structure.
Value-Based Pricing: Determining the price based on the perceived value to the customer, irrespective of the production cost. This strategy focuses on how much customers are willing to pay, often seen in luxury markets where brand and perceived quality drive pricing.
Value Chain Analysis: The process of separating a business operation into a series of value-generating activities in order to understand the activities that provide the business with a competitive advantage.
Value GROW Model: An extended coaching framework that adds a foundational step—Values—to the traditional GROW model (Goals, Reality, Options, Way Forward). It supports goal-oriented action by aligning team efforts with shared principles, fostering trust, and driving commitment to clear, measurable outcomes.
Value Net Framework: Developed by Brandenburger and Nalebuff, this model expands on Porter’s Five Forces by introducing ‘complementors’—entities that enhance the value of a firm’s product or service. It emphasises the importance of cooperative relationships alongside competitive ones in strategic planning.
Variable Cost: The cost associated with producing one additional unit of a product. Firms typically avoid setting prices below the variable cost to prevent losses.
Vertical integration: Refers to a form of diversification where a firm expands its business to different points in the supply chain. For example taking over a supplier (backwards vertical integration) or taking over a customer (forwards vertical integration).
Vertical integration, backward: A company engages in backward vertical integration when it purchases one or more suppliers that produce inputs that the company uses to produce final goods or services. For example, a car company might own a tire company, a glass company, or an engine manufacturer. Benefits of backward vertical integration include (1) creating stable supply, and (2) ensuring a consistent quality of inputs.
Virtue-signal: Publicly express opinions on an issue with the aim of demonstrating one’s moral superiority but without incurring any personal cost or taking any action to address the issue.
Walmart Effect: A situation where a single customer becomes the major purchaser of goods and services giving it substantial control of the market.
Wealth:
- Real wealth is discretionary time; money is merely the fuel (attributed to Alan Weiss).
- A measure of a person’s ability to survive so many number of days forward into the future if they were to stop working today (attributed to Robert Kiyosaki). For more information, read the article: What is an asset? What does it mean to be wealthy?.
Willingness to Pay: The maximum price a customer is willing to pay for a product or service. Understanding this is crucial for value-based pricing strategies.
🔴 Found these ideas useful?
Sharpen your edge
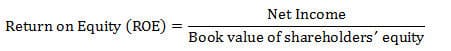
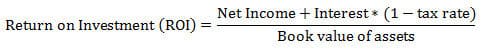
One reply on “Definitions”
[…] where connection and collaboration make products more valuable as more people use them (see network externalities). Entrepreneur and venture capitalist Marc Andreessen famously noted that “software is […]